Google Search Console provides the data needed to monitor your website’s performance and improve search rankings. This makes it indispensable for online businesses and entrepreneurs who want to maximize their success. If you want to dig deeper into more local seo tools, we also recommend you this guide.
Taking control of your search presence is easier to do when you use the free tools and reports.
1. What is Google Search Console?
Google Search Console is a free web SEO tool hosted by Google that provides a way for search marketers to monitor the overall status and performance of their sites in relation to Google search.
Important features:
- Monitor indexing and crawling.
- Identify and correct errors.
- Overview of search performance.
- Request indexing of updated pages.
- Review internal and external links.
It is not necessary to use Search Console to rank better. However, the usefulness of Google Search Console makes it indispensable to help improve search performance and drive more traffic to a website.
2. How to start using a Google Search Console Account
The first step in using Search Console is to verify site ownership.
Google provides several different ways to perform site verification, depending on whether you are verifying a website, a domain, a Google site, or a site hosted on Blogger.
Domains registered with Google domains are automatically verified when you add them to Search Console.
Most users will verify their sites using one of these four methods:
- HTML file upload.
- Metatag.
- Google Analytics tracking code.
- Google Tag Manager.
3. How to verify site ownership
There are two standard ways to verify site ownership with a normal website, such as a standard WordPress site.
- HTML file upload.
- Metatag.
When verifying a site using either of these two methods, you will choose the URL prefix properties process.
Let’s stop here and acknowledge that the phrase “URL prefix properties” means absolutely nothing to anyone but Google who came up with that phrase.
Don’t let that make you feel like you’re about to walk into a maze blindfolded. Verifying a site with Google is easy.
4. HTML file upload method
Step 1:
Go to Search Console and open the Property Selector drop-down menu that is visible in the upper left corner of any Search Console page.
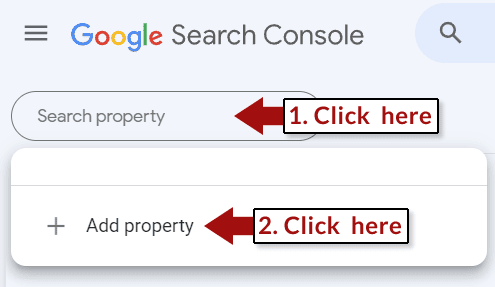
Step 2:
In the pop-up window labeled Select Property Type , enter the URL of the site and then click the Continue button.
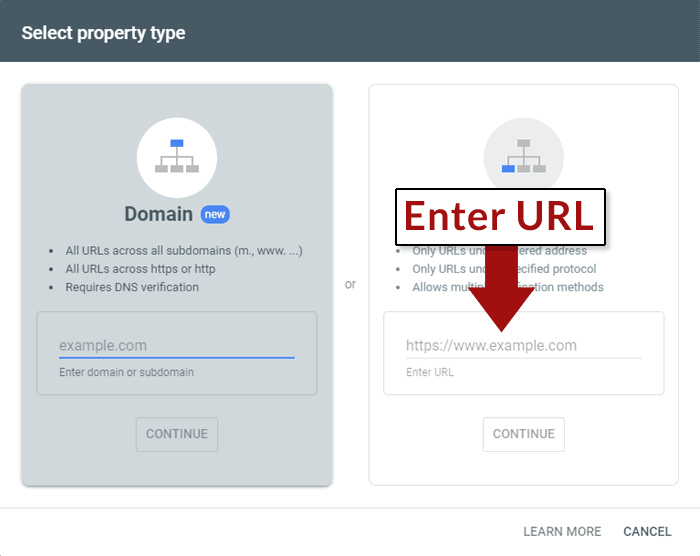
Step 3:
Select the HTML file upload method and download the HTML file.
Step 4:
Upload the HTML file to the root of your web site.
Root means https://example.com/. Therefore, if the downloaded file is named “verification.html”, then the uploaded file should be located at https://example.com/verification.html.
Step 5:
Finish the verification process by clicking Verify again in the search console.
5. URL inspection tool
The URL inspection tool shows whether a URL is indexed and eligible to be displayed in a search result.
For each URL submitted, a user can:
- Request indexing of a recently updated web page.
- See how Google discovered the web page (site maps and internal reference pages).
- View the last crawl date of a URL.
- Check whether Google is using a declared canonical URL or is using another one.
- Check mobile usability status.
6. Coverage
The coverage section shows how Google discovered the URL, shows whether Google successfully crawled the URL, and if not, provides a reason, and provides the status of the structured data.
The coverage section can be accessed from the menu on the left:
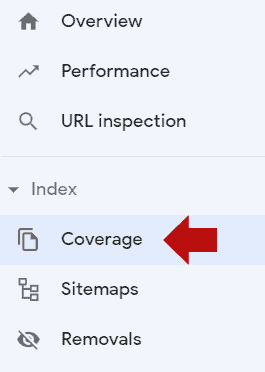
6.1. Coverage error reports
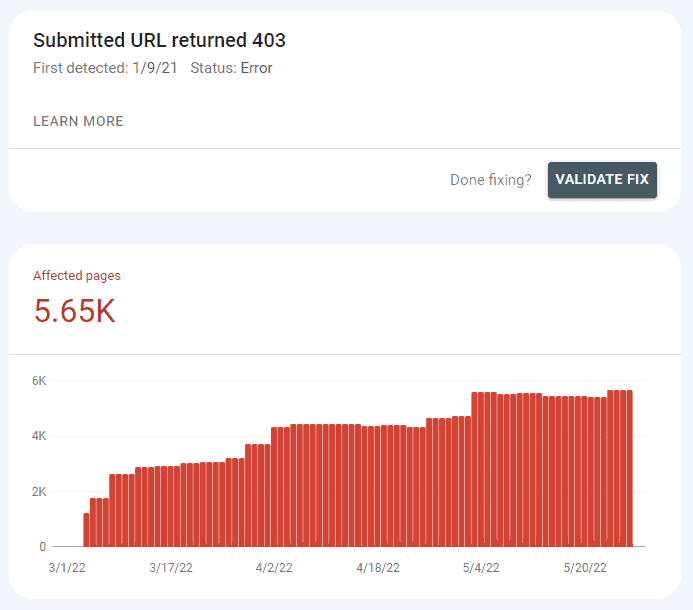
While these reports are labeled as errors, it does not necessarily mean that something is wrong. Sometimes it just means that indexing can be improved.
For example, in the screenshot below, Google shows a 403 forbidden server response to almost 6000 URLs.
The 403 error response means that the server is telling Googlebot that it is prohibited from crawling these URLs.
6.2. 404 error fix
A 404 server response is called an error only because the browser or crawler request for a web page was made in error because the page does not exist.
It does not mean that your site has an error.
If another site (or an internal link) links to a page that does not exist, the coverage report will show a 404 response.
Clicking on one of the affected URLs and selecting the Inspect URL tool will reveal which pages (or sitemaps) refer to the non-existent page.
Read more about SEO Optimization at: What is search engine optimization
7. GSC Features
7.1. Performance report
The top of the Search Console Performance Report provides multiple perspectives on a site’s performance in search, including on search features such as featured snippets.
There are four types of search that can be explored in the Performance Report:
- Web.
- Image.
- Video.
- News.
Google Search Console displays the type of web search by default.
Change the type of search displayed by clicking on the Search Type button:
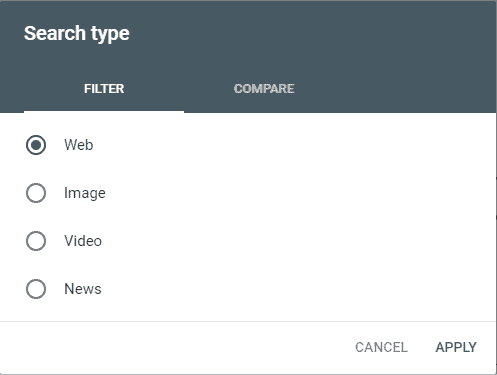
A useful feature is the ability to compare the performance of two search types within the graph.
Four metrics are prominently displayed at the top of the Performance Report:
- Total clicks.
- Total impressions.
- Average CTR (click-through rate).
- Average position.
By default, the Total Clicks and Total Impressions metrics are selected.
By clicking on the tabs dedicated to each metric, you can choose to view those metrics in the bar chart.
7.1.1 Impressions
Impressions are the number of times a website appeared in search results. As long as a user does not have to click on a link to view the URL, it counts as an impression.
Also, if a URL ranks at the bottom of the page and the user does not scroll to that section of the search results, it still counts as an impression.
High impressions are great because it means Google is showing the site in the search results.
But, the significance of the impressions metric is made meaningful by the Clicks and Average Position metrics.
7.1.2 Clicks
The click-through metric shows how often users clicked from the search results to the website. A high number of clicks plus a high number of impressions is good.
A low number of clicks and a high number of impressions is less good but not bad. It means that the site may need improvement to get more traffic.
7.1.3 CTR promedio
The average CTR is a percentage that represents the frequency with which users clicked from the search results to the website.
7.1.4 Average position
Shows the average position in the search results where the website tends to appear.
An average position at (20 to 29) means that the site appears on page two or three of the search results. This is not too bad. It simply means that the site needs additional work to give it that extra boost to the top 10.
7.2. Dimensions of the performance report
Scrolling down to the second part of the Performance page reveals several so-called Dimensions of a website’s performance data.
There are six dimensions:
7.2.1. Queries:
Displays top search queries and the number of clicks and impressions associated with each keyword phrase.
7.2.2. Pages:
Displays the best performing web pages (more clicks and impressions).
7.2.3. Countries:
Top countries (more clicks and impressions).
7.2.4. Devices:
It shows the main devices, segmented into mobile devices, desktops and tablets.
7.2.5. Search appearance:
Displays the different types of rich results in which the site was displayed. It also indicates whether Google displayed the site using Web Light results and video results, as well as associated clicks and impressions data. Web Light results are results optimized for very slow devices.
7.2.6. Dates:
The dates tab organizes clicks and impressions by date. Clicks and impressions can be sorted in ascending or descending order.
7.3. Keywords
Keywords are displayed in the Queries as one of the dimensions of the Performance Report (as noted above). The Queries report shows the top 1000 search queries that generated traffic.
Of particular interest are the low performing queries.
Some of these queries show low amounts of traffic because they are infrequent, known as long tail traffic.
But, others are search queries that result from web pages that could use improvement, perhaps could use more internal links, or could be a sign that the keyword phrase deserves its own web page.
It’s always a good idea to review underperforming keywords because some of them can be quick wins that, when the problem is fixed, can result in a significant increase in traffic.
7.4. Links
Search Console provides a list of all links pointing to the website.
However, it is important to note that the link report does not represent links that help rank the site.
It simply reports all links pointing to the website.
This means that the list includes links that do not help the site’s ranking. That explains why the report may show links that have a nofollow link attribute.
7.5. Site maps
A sitemap is usually an XML file that is a list of URLs that helps search engines discover web pages and other forms of content on a web site.
Sitemaps are especially useful for large sites, sites that are difficult to crawl if new content is added frequently.
Crawling and indexing are not guaranteed. Things like page quality, overall site quality, and links can have an impact on whether a site is crawled and pages are indexed.
Sitemaps simply make it easier for search engines to discover those pages and that’s it.
Remember, to improve your online presence and stand out on Google and Google Maps, having a review and customer experience management strategy can make all the difference. You can count on RAY, a comprehensive solution that can help you improve your Google reviews, rank high in search results and provide an exceptional customer experience.
8. Continue learning with these articles
Hopefully, by now you have a solid understanding of Google Search Console, you can continue reading more articles that will help your brand or business on our Blog.
